Effect of Dust on PV Modules
Solar panels are significantly affected by internal and external factors such as aging, radiation, shading, temperature, wind, pollution, and cleaning. Dust can be defined as small particles in crushed form smaller than 500 µm [1]. Dust can come from various sources such as construction sites, industrial plants, and dust storms. It consists of visible and invisible, floating and falling solid particles. The degree of efficiency degradation increases as the mass of dust particles accumulated on the surface of solar panels increases, leading to a reduction in power output and module efficiency.
Furthermore, as dust particle size decreases, smaller particles obstruct light transmission through the surface of the solar panel. As a result, power output decreases. The effect of contamination on incoming light on the glass is shown in Figure 1.
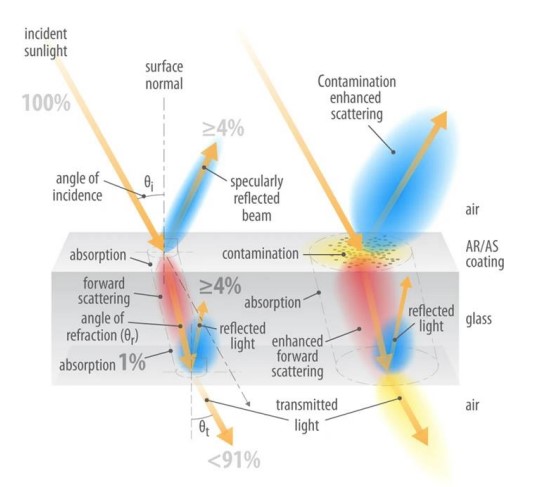

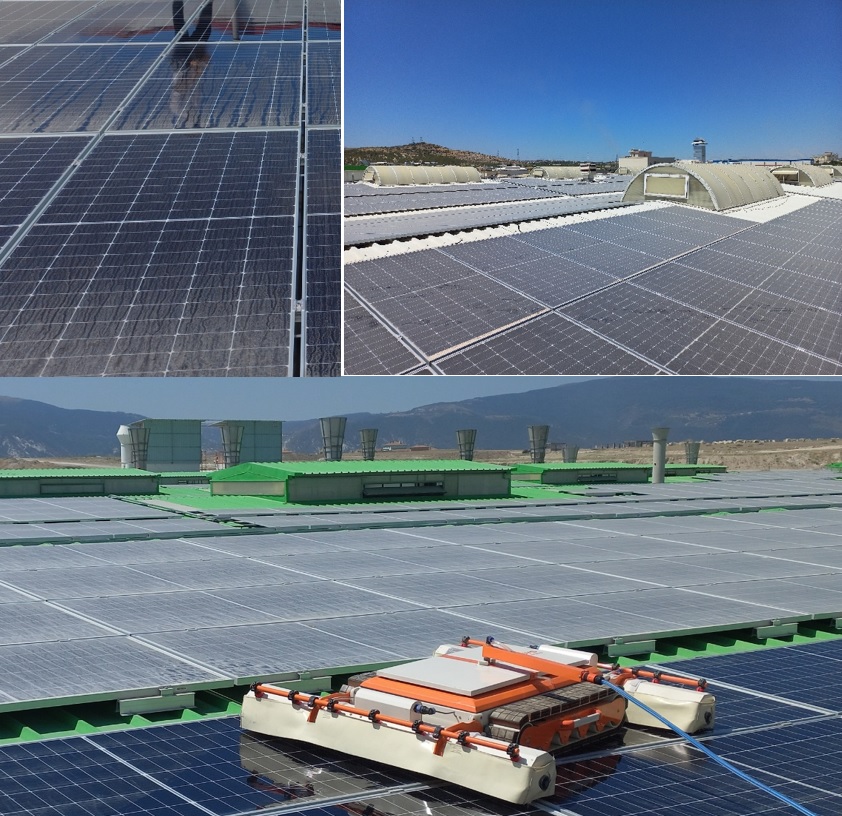
Different types of pollutants can include red soil, ash, sand, calcium carbonate, silica, etc. Air pollution can significantly affect the energy efficiency of solar panels. Even a short period after cleaning the panels, a decrease in energy production of 6.5% can occur. During long dry periods without rainfall, the energy loss due to dust accumulation can exceed 20%. Dust particles vary in terms of phase, type, chemical, and physical properties, depending on many environmental conditions. In addition to wind speed, air, humidity, and temperature play an important role in determining how dust is collected and deposited on solar panels [3]. Most researchers have studied the impact of dust accumulation on PV modules’ performance, and in these studies, it was observed that the performance of solar panels was significantly affected by the accumulation of red soil, limestone, and, finally, fly ash samples. When heavy layers of dust accumulate on the surface of solar panels, a significant reduction of about 10-20% in power output occurs. Figure 2 shows examples of dust accumulation. In the first image, in addition to dust, tire soot has covered the panel’s surface. The second image shows pollution caused by the flue gases from a textile company’s roof and nearby gas concrete plants. In the third image, the panels are covered with ceramic dust and other dust derivatives.


In a laboratory study, an artificial test was conducted on a 60 W solar panel using 100 W light and 7 different dust samples. In the test, three radiation levels of 650 / 750 / 850 W/m² were compared with 7 different samples. The comparison revealed a significant decrease in power output due to dust accumulation on the solar panel. Over a two-month period, a 4.7% decrease was observed, and in Saudi Arabia, a 40% decrease was observed over a six-month period [4].
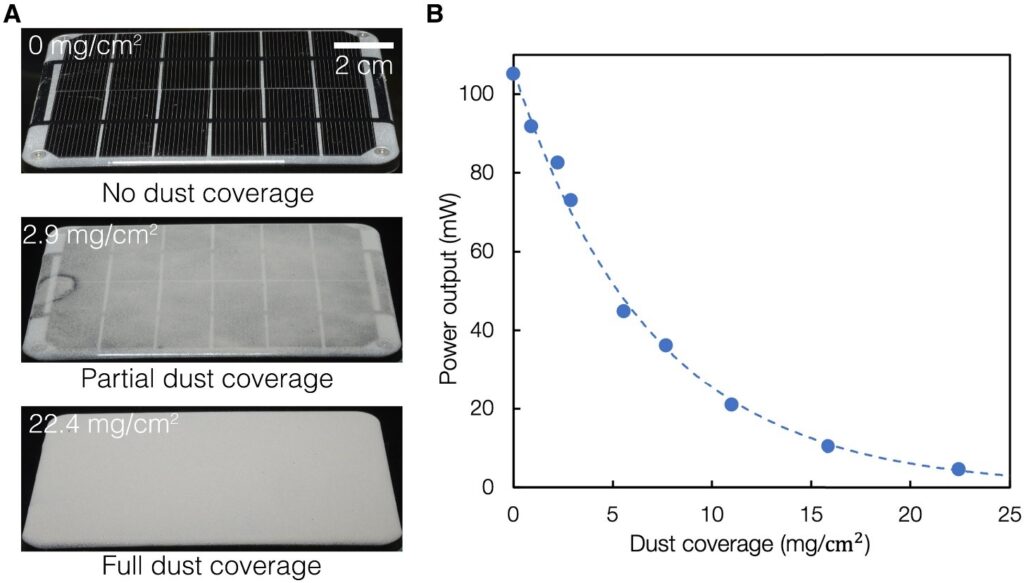

As a result, it was concluded that the average daily energy loss caused by accumulated dust on the PV module surface over a year is approximately 4.4%. During long dry periods without rainfall, the daily energy loss may exceed 20%. As the mass of dust accumulated on the module surface increases and particle size decreases, the module’s power output and efficiency decrease.
References:
- Dilip Kumar, Deepak Kumar, Chapter 12 – Dust Control, Editor(s): Dilip Kumar, Deepak Kumar, Sustainable Management of Coal Preparation, Woodhead Publishing, 2018, Pages 265-278.
- G. P. Smestad, T. A. Germer, H. Alrashidi, E. F. Fernández, S. Dey, H. Brahma, N. Sarmah, A. Ghosh, N. Sellami, I. A. I. Hassan, M. Desouky, A. Kasry, B. Pesala, S. Sundaram, F. Almonacid, K. S. Reddy, T. K. Mallick, and L. Micheli, “Modelling photovoltaic soiling losses through optical characterization,” Scientific Reports, vol. 10, no. 1, 2020.
- ZA Derwish, HA Kazem, K Sopian, MA Alghoul… – International Journal of Energy and Environment, 2013, “Impact of some environmental variables with dust on solar photovoltaic (PV) performance: review and research status.”
- T. Sarver, A. Al-Qaraghuli, L. L. Kazmerski, A comprehensive review of the impact of dust on the use of solar energy: History, investigations, results, literature, and mitigation approaches. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 22, 698–733 (2013).
Prepared by: Batuhan Mert LAÇİNKAYA
For your questions: batuhanlacinkaya@rob-sys.com
Date: 24.12.2024
The entire content of this website, including but not limited to code, design, text, images, videos, and all other elements, is protected under the provisions of Law No. 5846 on Intellectual and Artistic Works and applicable legal regulations. Any unauthorized copying, reproduction, dissemination, publication, or use of such content, whether for commercial or non-commercial purposes, shall result in legal proceedings.






